前言
为了更方便的使用Boost库,于是想到实现一个基于Boost离线文档的搜索引擎,对离线的HTML文件进行分析,、并对查询词进行分词(借用第三方库),然后根据相关性(简陋的相关性公式)进行排序,最终将查询结果用JSON的数据格式进行组织打包,最终通过对外的http服务将查询结果返回
成品效果以及GitHub链接
由于不怎么会前端的一些语法,所以页面比较简陋
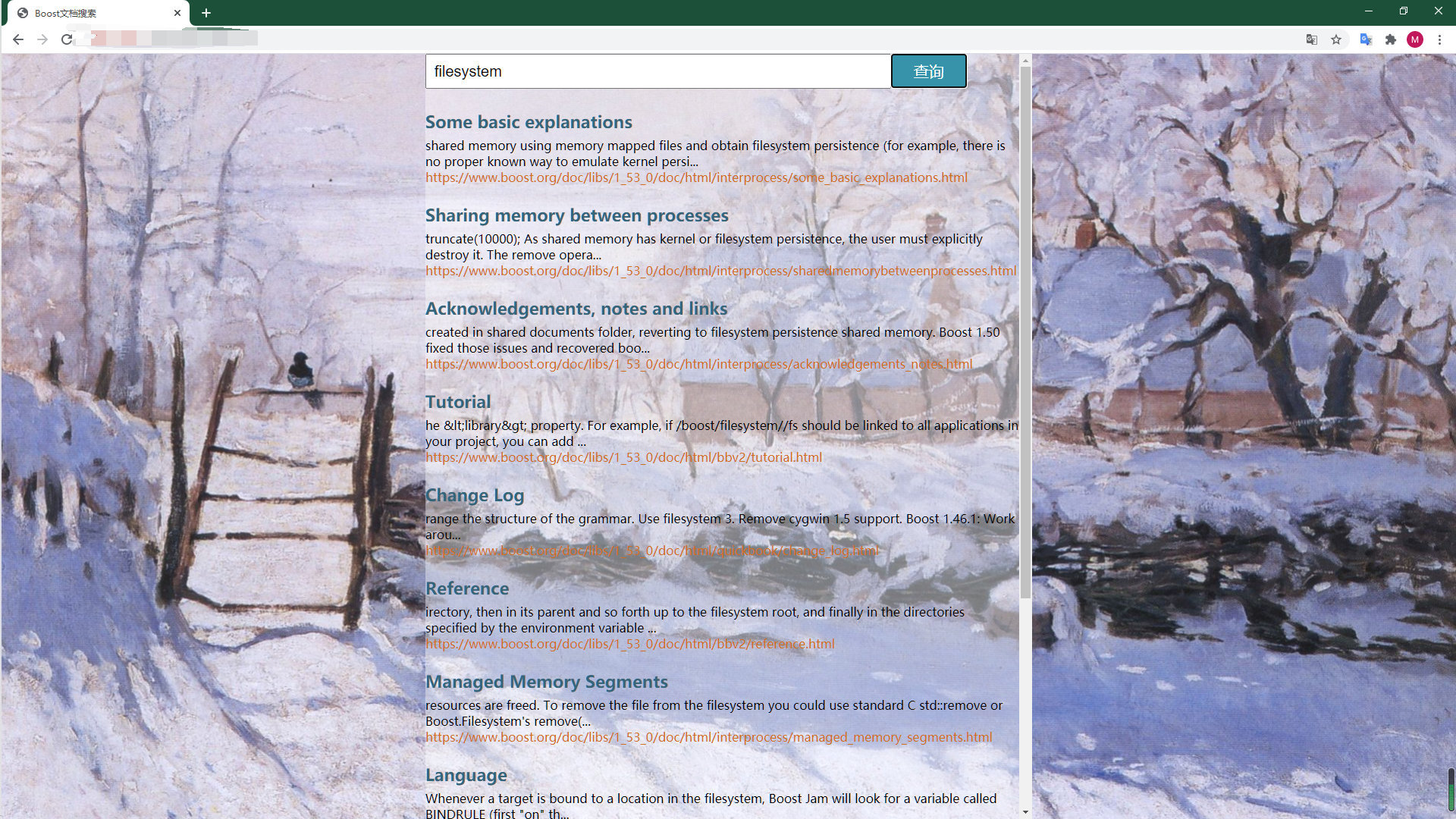
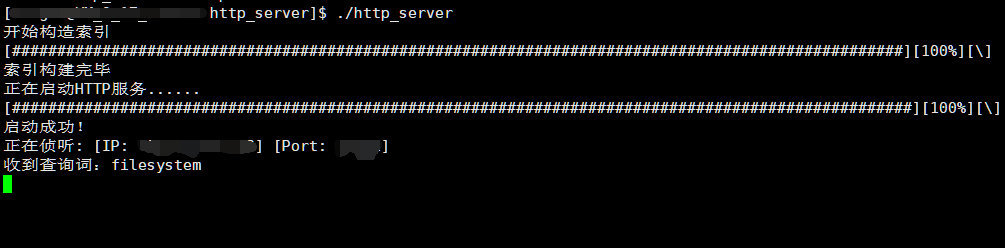
详细代码于 - GitHub链接:GitHub Boost-search-engine
整体结构
按照处理流程,整个项目的结构可以被分为,预处理模块,索引模块,搜索模块以及服务器模块
- 预处理模块:读取原始的HTML文档内容,进行预处理操作:解析一些重要的信息,如文档标题、文档的URL,文档的正文,即去除HTML标签,只保留正文;在预处理完毕之后,将结果整理成一个行文本文件,用以之后的模块使用
- 索引模块:将预处理好的行文本文件输入,根据预处理结果,在内存中构造正排索引(文档ID => 文档正文)和倒排索引(文档正文 => 文档ID)
- 搜索模块:输入查询词,先对查询词进行分词,然后实现触发,将查询结果按照相关性进行排序,依次拼装,按照JSON数据格式进行组织
- 服务器模块:加载搜索引擎模块,对外提供HTTP服务
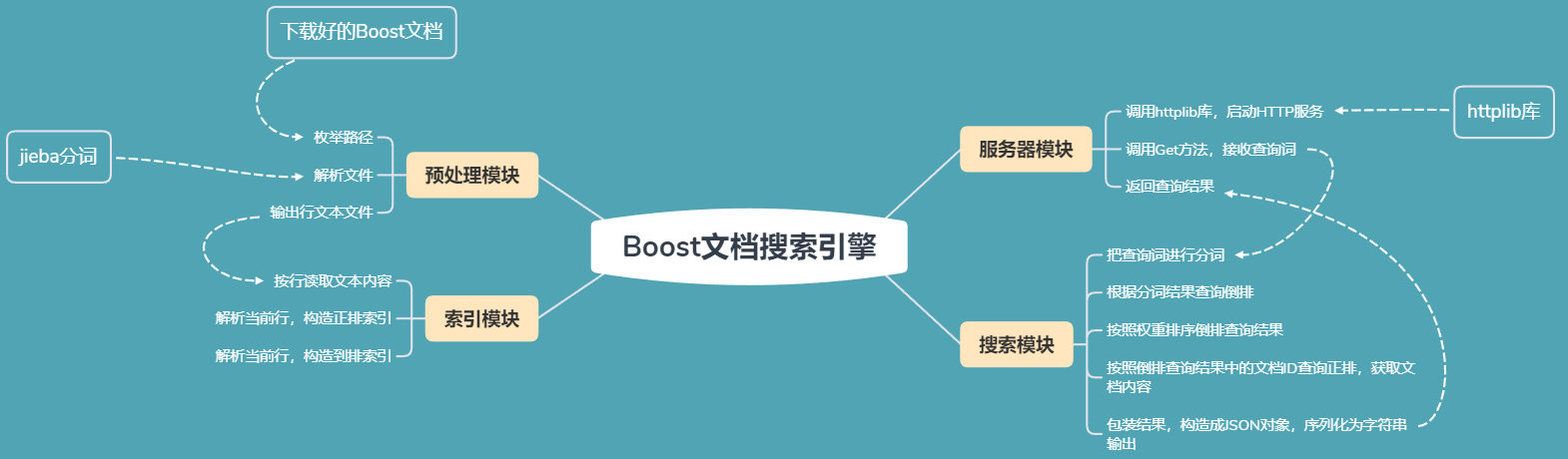
预处理模块
该模块核心功能为:读取并分析Boost文档的.html文件内容,解析出每个文档的标题,URL,正文,最终把结果输出为一个行文版文件
首先根据核心功能,定义一个可以表示一个文章的结构体,以及一些全局变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| string g_input_path = "../data/input/";
string g_output_path = "../data/tmp/raw_input";
struct DocInfo
{
string tittle;
string url;
string content;
};
|
枚举路径
使用Boost中的filesystem的递归文档迭代器来对每一个文件进行枚举,使用一个vector来临时存储,用于之后的解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| bool EnumFile(const string& input_path, vector<string>* file_list)
{
boost::filesystem::path root_path(input_path);
if( !boost::filesystem::exists(root_path) )
{
cout << "目录不存在" << endl;
return false;
}
boost::filesystem::recursive_directory_iterator end_iter;
for(boost::filesystem::recursive_directory_iterator it(root_path); it != end_iter; it++)
{
if( !boost::filesystem::is_regular_file(*it) )
continue;
if( it->path().extension() != ".html" )
continue;
file_list->push_back(it->path().string());
}
return true;
}
|
解析文件
- 遍历上一步vector中存放的文件路径,读取文件内容,将读取内容写入到string类型变量
html中
- 根据读取到的内容,首先解析出标题,按照html中的标签
<title></title>,调用string类成员函数substr获取文章标题
- 根据读取到的内容,构造对应的URL,由于网络路径和文件路径一致,所以只需要在文件的路径前加上前缀
https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_53_0/doc/即可
- 根绝读取到的内容,解析正文片段,跳过字符
<和字符>中的内容,同时将内容中的\n替换为空格(因为最终结果要对应到原始的html文档)
- 对于2、3、4步骤,解析出的三个内容使用不可见字符
\3分割,然后写入删除文件raw_put中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| bool ParseFile(const string& file_path, DocInfo* doc_info)
{
string html;
bool ret = common::Util::Read(file_path, &html);
if(!ret)
{
cout << "解析文件失败!" << file_path << endl;
return false;
}
ret = ParseTitle(html, &doc_info->tittle);
if( !ret )
{
cout << "标题解析失败" << endl;
return false;
}
ret = ParseUrl(file_path, &doc_info->url);
if( !ret )
{
cout << "url 解析失败" << endl;
return false;
}
ret = ParseContent(html, &doc_info->content);
if( !ret )
{
cout << "正文解析失败" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
|
索引模块
索引使用了正排索引和倒排索引,其结构体分别如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
struct DocInfo
{
int64_t _doc_id;
string _title;
string _url;
string _content;
};
struct Weight
{
int64_t _doc_id;
int _weight;
string _word;
};
|
创建一个类来表示整个索引结构,并提供外部调用的API
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Index
{
public:
Index();
const DocInfo* GetDocInfo(int64_t doc_id);
const vector<Weight>* GetInvertedList(const string& key);
bool Build(const string& input_path);
void CutWord(const string& input, vector<string>* output);
private:
DocInfo* BuildForward(const string& line);
void BuildInverted(const DocInfo& doc_info);
cppjieba::Jieba jieba;
private:
vector<DocInfo> _forward_index;
unordered_map<string, vector<Weight> > _inverted_index;
};
|
创建正排索引
正排索引使用vector来存放,文章的ID就是其所在位置的下标,元素内容就是预处理模块中的输出内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| DocInfo* Index::BuildForward(const string& line)
{
vector<string> tokens;
common::Util::Split(line, "\3", &tokens);
if( tokens.size() != 3 )
return nullptr;
DocInfo doc_info;
doc_info._doc_id = _forward_index.size();
doc_info._title = tokens[0];
doc_info._url = tokens[1];
doc_info._content = tokens[2];
_forward_index.push_back(move(doc_info));
return &_forward_index.back();
}
|
创建倒排索引
依次对标题与正文进行分词,建立统计词频的结构体,根据统计结果,填充Weight对象,其中成员_weight(权重)简单的设计了一个公式:权重 == 10 * 标题出现次数 + 正文出现次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
void Index::BuildInverted(const DocInfo& doc_info)
{
struct WordCnt
{
int _title_cnt;
int _content_cnt;
WordCnt()
: _title_cnt(0)
, _content_cnt(0)
{}
};
unordered_map<string, WordCnt> word_cnt_map;
vector<string> title_token;
CutWord(doc_info.title, &title_token);
for(string& word : title_token)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
++word_cnt_map[word]._title_cnt;
}
vector<string> content_token;
CutWord(doc_info.content, &content_token);
for (string word : content_token)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
++word_cnt_map[word]._content_cnt;
}
for(const auto& word_pair : word_cnt_map)
{
Weight weight;
weight._doc_id = doc_info.doc_id;
weight._weight = 10 * word_pair.second._title_cnt + word_pair.second._content_cnt;
weight._word = word_pair.first;
vector<Weight>& inverted_list = _inverted_index[word_pair.first];
inverted_list.push_back(move(weight));
}
}
void Index::CutWord(const string& input, vector<string>* output)
{
jieba.CutForSearch(input, *output);
}
|
至此,整个索引模块建立完成,内存中即存在了正排索引结构和倒排索引结构,等待搜索模块去调用
查询正排/倒排索引
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| const DocInfo* Index::GetDocInfo(int64_t doc_id)
{
if( doc_id < 0 || doc_id >= _forward_index.size() )
return nullptr;
return &_forward_index[doc_id];
}
const vector<Weight>* Index::GetInvertedList(const string& key)
{
auto it = _inverted_index.find(key);
if( it == _inverted_index.end() )
return nullptr;
return &it->second;
}
|
搜索模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Searcher
{
private:
Index* index;
public:
Searcher()
:index(new Index())
{}
bool Init(const string& input_path);
bool Search(const string& query, string* results);
private:
string GenerateDesc(const string& content, const string& word);
};
|
在使用搜索模块时,创建Searcher对象,即new了一个Index对象,接着调用成员函数Init,它会调用Index的成员函数Build,来创建正排索引和倒排索引,在需要查询时,调用成员函数Search,完成查询过程,将结果写入string类对象results中
搜索函数
搜索模块先对查询词进行分词,再根据分词结果去调用索引模块的查询正排,倒排成员函数,接着将查询结果按照权重降序排列,最后调用JSONCPP库函数来包装查询结果(同时调用相关函数来生成描述),序列化为字符串输出结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| bool Searcher::Search(const string& query, string* output)
{
vector<string> tokens;
index->CutWord(query, &tokens);
vector<Weight> all_token_result;
for(string word : tokens)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
auto* inverted_list = index->GetInvertedList(word);
if( inverted_list == nullptr )
{
continue;
}
all_token_result.insert(all_token_result.end(),
inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());
}
sort(all_token_result.begin(), all_token_result.end(),
[](const Weight& w1, const Weight& w2){
return w1.weight > w2.weight;
});
Json::Value results;
for(const auto& weight : all_token_result)
{
const DocInfo* doc_info = index->GetDocInfo(weight.doc_id);
Json::Value result;
result["title"] = doc_info->title;
result["url"] = doc_info->url;
result["desc"] = GenerateDesc(doc_info->content, weight.word);
results.append(result);
}
Json::FastWriter writer;
*output = writer.write(results);
return true;
}
|
至此,搜索模块就搭建好了,等待最终的服务器模块调用
服务器模块
首先初始化Searcher对象,调用Init成员函数初始化索引结构,然后调用Server对象中的Get方法,接收网页端请求,分析参数调用查询函数,然就将结果返回给网页端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| int main()
{
using namespace httplib;
searcher::Searcher searcher;
bool ret = searcher.Init("../data/tmp/raw_input");
if (!ret)
{
cout << "Searcher初始化失败" << endl;
return 1;
}
Server server;
server.Get("/searcher", [&searcher](const Request& req, Response& resp){
if (!req.has_param("query"))
{
resp.set_content("请求参数错误", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
return;
}
string query = req.get_param_value("query");
cout << "收到查询词:" << query << endl;
string results;
searcher.Search(query, &results);
resp.set_content(results, "application/json; charset=utf-8");
});
server.set_base_dir("./www");
server.listen("x.x.x.x", [port]);
return 0;
}
|
至此,整个搜索引擎已经搭建完成,只需要运行起来即可


